Introduction
I often get asked, "What inspired you to turn your professional attention to face masks?" I became an audiologist because even as a child I knew I wanted to help improve the lives of people living with hearing loss. My dad had a unilateral hearing loss and was not motivated to do anything about it despite the impacts on his relationships at home and at work. I realized early on that to change health behavior, a public health approach would be necessary. Hence, my early epidemiological research focused on hearing screening and measurement of self-reported hearing difficulties to identify those in need of some form of audiological intervention. Fast forward to March 2020: I live in New York City, the COVID-19 epicenter at the time, and I felt powerless and desperate to help in any way I could, albeit from a distance. A light bulb went off in my head when I recalled an experience with my 92-year-old aunt who has hearing loss and has been hospitalized on several occasions. We were in the emergency department of a large and impersonal New York City hospital right before NYC closed down. The most popular words spoken by the patients and families around us during our six hours in the emergency area were “What did you say? I cannot hear or understand what you are saying!” The health care providers (HCP) were all wearing masks. My aunt and all the other patients could not understand a word being spoken. In our case, the HCP’s looked to me to interpret as it was easier than trying to communicate with her.
Later, while sheltering in place at home in my apartment I decided to conduct a simple experiment. I asked my husband to speak the Rainbow Passage without and while wearing his mask. Using my NIOSH sound level meter app, I noted that the reduction in sound pressure level (SPL) when he was wearing the mask was substantial. The results from this DIY experiment were intriguing, but far from scientifically defensible.
SPL of Speech Through a Face Mask
When I measured the sound pressure level of speech through a face mask, the output SPL appeared to differ by frequency, seemingly because of the filtering effect of the cloth mask I asked him to wear. I theorized that audibility and clarity of speech would be impacted and that communication access would be very much compromised. I also postulated that social distancing would interact with masking effects and further compromise speech intelligibility.
Let's consider a little primer on virology and the policies necessary to mitigate the spread of COVID-19. The unique characteristic of this virus is the route of transmission via small droplets ejected from the mouth. The droplets are expelled when a person with COVID-19 coughs, sneezes, or speaks. Interestingly, speaking actually produces more droplets than does coughing (Chao et al., 2009), and louder speech creates a relatively larger quantity of droplets than does softer speech (Anfinrud, Bax, Stadnytski, & Bax, 2020). When a person speaks, he or she releases nearly 200 viral particles per minute! Thus, it would take five minutes of speaking face to face to receive the dose of particles to readily infect a conversation partner.
Facemasks and COVID-19
COVID-19 can spread quite easily. As you probably already are aware, an individual can become infected with COVID-19 when breathing in the droplets expelled by a person infected with the virus. The person infected with the virus may be symptomatic or asymptomatic. How much virus is released also depends upon airflow and ventilation in a space, as well as the distance from the infected person. Indoor spaces and close quarters are areas where the virus can spread more easily. Given the distance the droplets travel, people are encouraged to remain at least one meter away from each other when speaking face to face. In fact, two meters or the equivalent of six feet when communicating is preferable. Wearing a mask was deemed essential in many settings, including hospitals.
Social Distancing
Social distancing impacts communication as it is harder to hear from farther away. The inverse square law relates directly to the social distancing recommendation. The inverse square law asserts that a specified physical quantity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source of that physical quantity. Applied to speech acoustics, we know that for every doubling of the distance from the sound source in a free field situation, the sound intensity will diminish by 6 decibels. To say that another way, sound diminishes by approximately 6 dB for each doubling of distance. For example, if you are 2' away from someone who is speaking and move to 4' away, thus doubling the distance, the person's voice will be reduced by 6 dB. Therefore, health care provider and patient communication in a variety of medical settings will be negatively impacted because of both the social distancing and masking requirements.
Audibility
My home experiment indicated that a face mask might affect audibility, and we also know social distancing definitely reduces audibility. Before I go into quantifying these effects, let's revisit some basic speech acoustics and then relate this to the filtering effects of face masking and the impact on speech clarity. First of all, masking reduces airflow, and with the mouth covered, sounds are no longer visible on the lips. The low-frequency vowel sounds are easiest to hear as they are higher in intensity. In contrast, consonant sounds are higher in frequency and lower in intensity, and so they are more difficult to detect. Notably, not all consonant sounds are created equal. The consonant sounds which are both weak in intensity and high in frequency are difficult to hear (e.g. /p/). Under most circumstances, they are visible on the lips allowing for visual clues to supplement the auditory cues, which may be inaudible with a mask. The bottom line is that face masks not only have attenuation effects thus reducing speech volume, but they also degrade speech quality and hide facial expressions/cues that are critical to speech comprehension. While hearing health care professionals are aware of the detrimental effects of face masking as it relates to speech understanding, we also have to keep in mind the collateral damage posed by strategies in place to mitigate the spread of the virus, especially on certain high-risk populations.
Older Adults
Older adults are highly susceptible to the disease and are at higher risk for fatal consequences. The risk of mortality from COVID-19 increases from 3.6% for people in their 60s to 14.8% for those 70 years of age and older (Oxford COVID ‐19 Evidence Service, 2020). Older adults with co-morbidities including cardiovascular disease and diabetes are most vulnerable to COVID-19. Of course, age-related hearing loss is co-morbid with many of the conditions placing older adults at increased risk for COVID-19. Older adults, therefore, will be disadvantaged because of age-related changes in hearing for high-frequency sounds and because of the multiple comorbidities associated with advancing age.
Impacts of Face Masking on Speech Understanding
You might wonder how I could formally research the impacts of face masking on speech understanding while I was sheltering in place in the epicenter of the pandemic. Coincident with my curiosity being aroused, I received an email from a colleague in Israel. He wanted to update me on some of the advanced technological solutions for hearing enhancement offered by Alango Technologies, where he serves as the CEO. I asked if he could make some of the face mask measurements I was interested in researching. In less than 36 hours, he and his colleague made the measurements, and we published the results in an article for Hearing Review (Goldin, Weinstein, & Shiman, 2020). We decided to quantify measured voice samples in an anechoic chamber as a function of the type of mask being worn. The masks we used ranged from a simple medical mask to the N95 mask. We used a GRAS head and torso simulator to play white noise through its artificial mouth. The output acoustic signal was measured by a microphone at 2 meters distance.
Did your findings dovetail with your hypothesis?
We found that the efficiency and effectiveness of some of the masks being used in medical settings not only differ in terms of transmission of the COVID-19 virus but also in terms of transmission of speech sounds. Medical face masks essentially serve as a low-pass filter, attenuating the high frequencies (2000-7000 Hz) where most of the energy for the high-pitched consonants so critical to speech understanding resides (Goldin, Weinstein, & Shiman, 2020). The audibility of consonants is significantly diminished when these masks are worn. The impact on persons with hearing loss trying to understand someone speaking through one of these masks is therefore quite dramatic. In short, with face masking, the high-frequency consonant sounds will now often be rendered inaudible, and they are also not visible on the lips when a mask is worn. Not surprisingly, therefore, communication accuracy and access are severely compromised.
Do you have the data showing the differences across the masks you tested?
Figure 1 provides a nice summary (Goldin, Weinstein, Shiman, 2020). The traditional medical mask attenuates sound by 3 to 4 decibels, while the level of degradation was close to 12 dB for the N95 mask. It is abundantly clear that the speech quality degradation, in combination with room noise/reverberation, social distancing, and the absence of visual cues, will render speech close to unintelligible for many people being treated in both inpatient and ambulatory care settings.
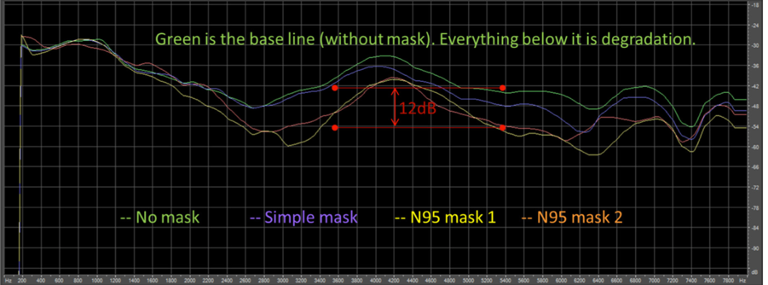
Figure 1. Frequency-specific degradation of the input signal for different types of face masks. The upper green response is the reference (no mask). Data obtained from a GRAS head and torso simulator playing white noise through its artificial mouth. The output acoustic signal was measured by a microphone at 2 meters distance.
Masking Alternatives
There are some masking alternatives on the horizon. At the same time we published our article, a college student gained notoriety for the clear masks she began to produce to compensate for the loss of visibility when wearing traditional medical masks. Some hospital-based practices and some hearing aid companies also began to fabricate clear masks. With audiologists returning to their practices, and the communicative problems posed by face masking having become an issue for both health care providers and patients, there is now a demand for clear plastic masks so that mouth and facial expressions are more visible to our patients. The home-made transparent masks are problematic in terms of droplets adhering to the plastic and fogging. Also, many of the non-FDA approved clear masks do not fit the nose and mouth tightly and some apparently cause difficulty breathing. We are now studying the acoustic effects/advantages of the variety of clear masks worn by laypeople and hearing health care professionals, as well as the FDA-approved masks on the market.
Clear Masks
Clear masks are also on the market. The Communicator TM Surgical Mask with a Clear Window (Model FM86000) manufactured by Safe N’Clear is a patented FDA registered device that meets ASTM F2100 Level 1 protection surgical mask standards. It includes a fog-resistant clear window for improved communication. As you might expect the COVID-19 pandemic disrupted mask manufacturing efforts domestically and globally. These masks are made in the USA and were back-ordered through mid-July, but will likely be available by the time you read this article.
Other Variables
As we enter this "new normal of face masking," there are several variables that come to mind when assessing masks and speech understanding. These include (1) background noise, (2) signal-to-noise ratio, (3) reverberation time, and, (4) novelty of hospital environments, which are threatening and stressful. Pichora Fuller (2016) aptly introduced the acronym “NUTS” to describe stressful listening situations such as hospitals which are: Novel/Noisy, Unpredictable, Threatening, and a challenge to one’s sense of Self-efficacy. The absence of supportive social networks to help persons with hearing loss negotiate when hospitalized or when speaking with health care professionals of course adds extra stress. And, during COVID-19, many medical centers have instituted visitor restrictions. Caregivers and others who would typically provide communication assistance or emotional support to patients on medical visits are now required to wait outside of the facility or in designated areas away from the patient and the medical providers. This adds more stress to the equation for patients, which can negatively impact communication.
Settings and Situations With Greatest Impact
The impacts of communication breakdowns due to facial masking can be felt in a variety of health care settings. These include: (a) ambulatory and inpatient care settings (b) palliative care setting, and (c) emergency departments. In addition, communication access will be impacted during transitions in care including emergency department triage, inpatient (ICU) triage, and for incident (multi-casualty) triage protocols. I should also add that when persons with hearing loss encounter first responders (e.g. ambulance drivers and fire persons) masking will impact communication exchanges, safety, and welfare. As we know, the rights of persons with disabilities are protected by Federal Law. The Americans with Disability Act (ADA) of 1990 mandates communication accessibility for hospitals and other medical facilities. The US Supreme Court decided in its 1999 Olmstead decision that the ADA requires the provision of services to individuals with disabilities in the most integrated setting appropriate to their needs.
General Patient-Clinician Communication
Patient-clinician communication is a favorite topic of mine and one which has been gaining a great deal of attention. First, let me emphasize that inaccessible and inadequate patient-clinician communication has always jeopardized the care of persons with sensory disabilities. COVID-19 has exacerbated the situation. Let me add that hearing loss and physician-patient communication are rarely connected in the literature even though we know that hearing loss has an important influence on the quality of communication. And, correcting hearing loss significantly improves communication access (Cohen et al., 2017). We conducted a structured literature search that revealed that hearing loss has been largely overlooked in studies of clinician-patient communication and is rarely mentioned as a contributor to misunderstandings/mishearings in health care settings, which are vectors for ineffective communication. Since the capacity to receive verbal information is compromised in patients with hearing loss, it is not surprising that health care outcomes are compromised as well (Mormer, Cipkala-Gaffin, Bubb, & Neal, 2017). In addition, the inpatient hospital experience, length of stay, and need or rehospitalizations are directly impacted by hearing loss (Chang, Weinstein, Chodosh, & Blustein, 2018; Mormer et al., 2017). Culling from a sample of participants in the Medicare Current Beneficiary Survey (MCBS), we found that 11.6% characterized their hearing difficulties as being "sufficiently severe", meaning that they had trouble communicating with their doctor or other medical personnel (Chang et al., 2018). Those who reported trouble communicating had, on average, 32% greater odds of hospital readmission. Simply put, inadequate patient-clinician communication likely compromises history taking, shared-decision making, information transfer (e.g. understanding of discharge instructions), patient autonomy, and self-management. Of course, our audiology practices will be directly affected, in innumerable ways. The pandemic is in our rear and front view mirrors and audiologists must be included in the mix in top-down discussions regarding communication access. Communicating with people with sensory loss must be as effective as communication with those without sensory loss.
Tips to Optimize Communication in Health Care Settings
We are all aware of the reasonable assists available for optimizing hearing and communication during routine clinical encounters. Let’s develop and disseminate information about universal communication strategies or precautions health care professionals should adopt to improve communication with their patients. As part of the routine audiology encounter, make sure to encourage your patients to be proactive and inform their physician/health care provider how best to communicate with them. It is imperative that you emphasize to your patients that a better understanding of their health issues will promote collaborative communication and improved outcomes. It will also enable their physician to be more supportive and will help to optimize adherence to the treatment processes (Cohen et al., 2017). Also, the provision of communication concordant care and innovative communication solutions such as the use of communication devices, smartphones, and speech-to-text apps is imperative. I encourage my patients to tell ALL healthcare providers that they have a hearing loss and to place their Communication Access Plan (CAP) in their electronic medical record (https://www.hearingloss.org/wp-content/uploads/HLAA_HC_CAP_Form_and_Instructions.pdf). Finally, become part of multi-disciplinary teams working to impose system-level sustainable changes essential for communication accessibility.
Strategies for Communicating When Wearing a Mask
Here is a top ten list of strategies to help with communication when wearing a mask. Notably, many of the strategies we typically recommend are not applicable when wearing a mask. My mask list is as follows:
- Reduce the level of background noise as much as possible when communicating.
2. Talk slowly and raise the level of your voice slightly.
3. Try to secure the attention of the person to whom you are speaking with a slight tap on the shoulder.
4. Take turns when speaking; do not interrupt the person speaking.
5. Use portable/handheld amplification devices to help with communication for persons with hearing loss who do not use hearing aids, and when possible use a whiteboard as applicable.
6. Provide large-print material to supplement what has been verbally communicated.
7. Use speech-to-text apps, which translate speech into text in real-time, with a smartphone, including hearing aids apps when applicable.
8. Face the listener. If using a clear mask with facial features visible, stand so the listener can clearly see your face.
9. Always ask patients the best way to communicate with them.
10. Try not to talk to the patient while walking with them.
Thoughts on the Impacts on Children and Adults When Returning to the Classroom
I am especially concerned about “communication access” for stakeholders in educational settings ranging from pre-kindergarten to college to graduate/professional schools. Educators will have to adopt the policies regarding masking and social distancing while at the same time adhering to various federal guidelines and considering the rights of persons with disabilities. Numerous federal guidelines, namely Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, as amended, 29 U.S.C. § 794 (Section 504), the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) of 1990, and the Stafford Act of 1988 relate directly to persons who are hard of hearing, deaf, or have dual sensory impairments. The challenge to school administrators will, of course, be to avoid discrimination on the basis of disability while continuing to cooperate with public health authorities ensuring that students and educators with disabilities in all educational settings have full access in the classroom.
Students, especially those with varying degrees of hearing loss, will miss learning opportunities with the degraded speech signal from face masks, the elimination of lipreading and speaker expressions with face masks, and social distancing (American Cochlear Implant Alliance, 2020). It is important to underscore that speaking and listening are the primary communication modes in auditory learning environments, and 75% of the school day involves listening activities.
The American Cochlear Implant Alliance has recently shed light on considerations relating to educational access, including the use of face shields which meet CDC recommendations to cover the front and sides of the face (extend to the chin or below, with no exposed gap between the forehead and the shield's headpiece), and provide barrier protection (Perencevich, Diekema, & Edmond, 2020). It is noteworthy that when physically distancing (6 feet), face shields reduce inhaled virus by 92% (Mundell, 2020). The ACI has excellent guidance on the use of face shields https://www.
Final Take-Aways
We should take advantage of every opportunity to increase awareness and offer resources to promote effective communication among people of all ages and in all settings during this health crisis. Communication access and the need for humans to communicate responsibly and effectively is a right that we are very well qualified to help optimize.
References
Anfinrud, P., Bax, C., Stadnytski, V. & Bax, A. (2020). MedRxiv. Preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.02.20051177.
American Cochlear Implant Alliance (2020). Consideration of face shields as a return to school option. Available from www.acialliance.org
Chang, J., Weinstein, B., Chodosh, J., & Blustein, J. (2018). Hospital readmission risk for patients with self-reported hearing loss and communication trouble. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 66(11), 2227-2228. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.15545
Chao, C.Y.H., Wan, M.P., Morawska, L., Johnson, G.R., Ristovski, Z.D., Hargreaves, M.,...Katoshevskig, D. (2009). Characterization of expiration air jets and droplet size distributions immediately at the mouth opening. J Aerosol Sci, 40(2), 122-133. doi:10.1016/j.jaerosci.2008.10.003
Cohen, J., Blustein, J., Weinstein, B., Dischinger, H., Sherman, S., Grudzen, C., & Chodosh, J. (2017). Studies of physician-patient communication with older patients: How often is hearing loss considered? A systematic literature review. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 65, 1642-1649. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.14860
Goldin, A., Weinstein, B., & Shiman, N. (2020). How do medical masks degrade speech reception? Hearing Review, 27, 8-9.
Mick, P., Foley, D., & Lin, F. (2014). Hearing loss is associated with poorer ratings of patient-physician communication and healthcare quality. J Am Geriatr Soc, 62(11), 2207-2209.
Mormer, E., Cipkala-Gaffin, J., Bubb, K., & Neal, K. (2017). Hearing and health outcomes: Recognizing and addressing hearing loss in hospitalized older adults. Seminars in Hearing, 38(2), 153–159. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0037-1601570
Mundell, E.J. (2020). Should face shields replace face masks to ward off coronavirus? WebMD news. Available at www.webmd.com
Perencevich, E.N., Diekema, D.J., & Edmond, M.B. (2020). Moving personal protective equipment Into the community: Face shields and containment of COVID-19. JAMA, 10.1001/jama.2020.7477. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.7477
Pichora-Fuller, M. (2016). How social psychological factors may modulate auditory and cognitive functioning during listening. Ear and Hearing, 37 Suppl 1, 92S-100S. 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000323.
Citation
Weinstein, B. (2020). Face masks and communication - audiological implications. AudiologyOnline, Article 27291. Available at www.audiologyonline.com
